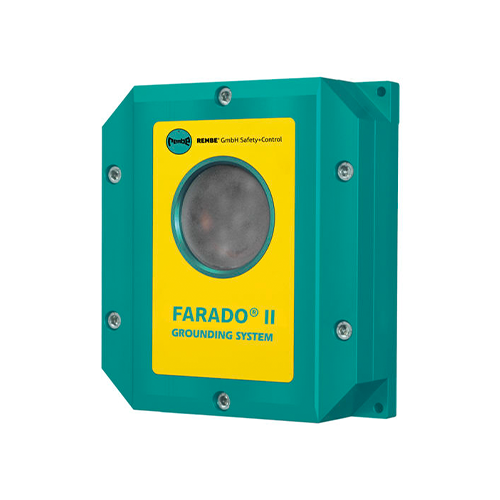
FARADO® II Grounding System
Mechanism
Electrostatic charges can build up because of the friction when flammable liquids, gases or solids are being conveyed. The resulting electrostatic discharges e.g. sparks can be a risky ignition source for explosive atmospheres under the appropriate conditions. The FARADO® II continuously dissipates the electrostatic potentials to prevent these discharges.
The grounding clamp is connected to the object that must be grounded. When the FARADO® II detects the grounded tank, the pumps, valves, or mechanical conveyors connected to the grounding relay will be activated for the filling process. The connection between the clamp and the object is permanently monitored. If a fault occurs or if the clamp’s connection becomes disconnected, then the grounding relay will generate a corresponding signal and the filling process will be stopped.
The FARADO® II also monitors the capacitance of the connected object as well as the connection‘s resistance. No activation will be given if they do not exceed the preset limit values. Insufficient capacitance means that the grounding clamp is not connected to the specific object but is possibly connected to a smaller or already grounded object.
Application
The self-monitoring FARADO® II grounding system was developed for grounding when filling or emptying mobile containers such as tank trucks, IBCs, FIBCs, drums, etc., and it is used in the chemical, food, pharmaceutical, cosmetics, oil, and gas as well as wood industries.